Abstract
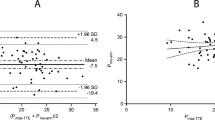
Objective: To examine the usefulness of preload indices obtained by transoesophageal echocardiography (TOE) for estimating stroke volume at various levels of cardiac index. Design: Prospective clinical study. Setting: Intensive care unit with surgical patients. Patients: 16 ventilated patients monitored via Swan-Ganz catheterization and TOE. Interventions: Echocardiographic images of left ventricular cross-sectional short-axis areas were analysed for the preload indices end-diastolic area (EDA), stroke area and end-diastolic wall stress. The relation between these indices and stroke volume, calculated from thermodilution cardiac output, was analysed in all patients and in nine patient groups discriminated by various ranges in heart rate (≤ 70 to > 110 beats/min), pulmonary artery occlusion pressure (≤ 8 to > 12 mm Hg) and cardiac index (≤ 3.0 to > 4.2 l/min per m2). Measurements and results: Overall stroke volume (n = 155) correlated significantly (p < 0.0001) with EDA (r = 0.89) and stroke area (r = 0.80). The correlation with end-diastolic wall stress was non-significant (r = 0.51). Linearity in the relation between stroke volume and EDA or stroke area was independent of variations in heart rate and pulmonary artery occlusion pressure. Stroke volume correlated well with EDA and stroke area, when cardiac index was normal or high, but the relation slightly deteriorated (r = 0.63 to ≤ 0.72) when the cardiac index was low. Changes in EDA and stroke area by more than 1, 2 or 3 cm2 were weak predictors for changes in stroke volume greater than 20 %. Conclusions: Stability of the relation between echocardiographic preload indices and stroke volume emphasize the potential of TOE for continuous preload monitoring in the critically ill.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 11 April 1996 Accepted: 2 January 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Greim, CA., Roewer, N., Apfel, C. et al. Relation of echocardiographic preload indices to stroke volume in critically ill patients with normal and low cardiac index. Intensive Care Med 23, 411–416 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001340050349
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001340050349