Abstract
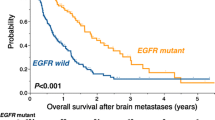
Mutated epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and signaling pathways were associated with multiple brain and intra-pulmonary metastases, oncogenic progression and metastasis. However, features of metastasis to other organs and the independent prognostic influence of metastatic lesions were not elucidated in patients with lung cancer harboring EGFR mutations. Between January 2007 and April 2012, we treated 277 patients diagnosed with stage IV lung adenocarcinoma. Studied were 246 patients with available tumor EGFR mutation data who also underwent radiographic evaluation of lung, abdominal, brain, and bone metastases. The EGFR mutated group (N = 98) had significantly more metastatic lesions in the brain and bone than the wild-type group (N = 148): brain, 3 (1–93) versus 2 (1–32) median (range), P = 0.023; bone, 3 (1–43) versus 2 (1–27), P = 0.035, respectively. In addition, EGFR mutations were significantly more frequent in patients with multiple than non-multiple lung metastases (24/40 vs. 12/42, P = 0.004). Multivariate analysis showed that bone metastasis was a significant independent negative predictive factor of overall survival (OS) in patients with mutated [hazard ratio (HR) 2.04; 95 % confidence interval (CI) 1.17–3.64; P = 0.011] and wild-type EGFR (HR 2.09; 95 % CI 1.37–3.20; P < 0.001). In conclusion, patients with mutated EGFR had more lung, brain, and bone metastases, and bone metastasis was an independent negative predictor of OS.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamamoto H, Toyooka S, Mitsudomi T (2009) Impact of EGFR mutation analysis in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 63(3):315–321
Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K et al (2010) Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med 362(25):2380–2388
Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y et al (2010) Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 11(2):121–128
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S et al (2009) Gefitinib or carboplatin–paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 361(10):947–957
Larsen AK, Ouaret D, El Ouadrani K et al (2011) Targeting EGFR and VEGF(R) pathway cross-talk in tumor survival and angiogenesis. Pharmacol Ther 131(1):80–90
Lichtenberger BM, Tan PK, Niederleithner H et al (2010) Autocrine VEGF signaling synergizes with EGFR in tumor cells to promote epithelial cancer development. Cell 140(2):268–279
Yatabe Y, Takahashi T, Mitsudomi T (2008) Epidermal growth factor receptor gene amplification is acquired in association with tumor progression of EGFR-mutated lung cancer. Cancer Res 68(7):2106–2111
Barr S, Thomson S, Buck E et al (2008) Bypassing cellular EGF receptor dependence through epithelial-to-mesenchymal-like transitions. Clin Exp Metastasis 25(6):685–693
Sekine A, Kato T, Hagiwara E et al (2012) Metastatic brain tumors from non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR mutations: distinguishing influence of exon 19 deletion on radiographic features. Lung Cancer 77(1):64–69
Eichler AF, Kahle KT, Wang DL et al (2010) EGFR mutation status and survival after diagnosis of brain metastasis in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Neuro-oncology 12(11):1193–1199
Wu SG, Hu FC, Chang YL et al (2013) Frequent EGFR mutations in nonsmall cell lung cancer presenting with miliary intrapulmonary carcinomatosis. Eur Respir J Off J Eur Soc Clin Respir Physiol 41(2):417–424
Schouten LJ, Rutten J, Huveneers HA et al (2002) Incidence of brain metastases in a cohort of patients with carcinoma of the breast, colon, kidney, and lung and melanoma. Cancer 94(10):2698–2705
Delea TE, McKiernan J, Brandman J et al (2006) Impact of skeletal complications on total medical care costs among patients with bone metastases of lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol Off Publ Int Assoc Study Lung Cancer 1(6):571–576
Park JH, Kim TM, Keam B et al (2013) Tumor burden is predictive of survival in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and with activating epidermal growth factor receptor mutations who receive gefitinib. Clin Lung Cancer 14(4):383–389
Welsh JW, Komaki R, Amini A et al (2013) Phase II trial of erlotinib plus concurrent whole-brain radiation therapy for patients with brain metastases from non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 31(7):895–902
Komatsu T, Kunieda E, Oizumi Y et al (2012) An analysis of the survival rate after radiotherapy in lung cancer patients with bone metastasis: is there an optimal subgroup to be treated with high-dose radiation therapy? Neoplasma 59(6):650–657
Bae HM, Lee SH, Kim TM et al (2012) Prognostic factors for non-small cell lung cancer with bone metastasis at the time of diagnosis. Lung Cancer 77(3):572–577
Bearz A, Garassino I, Tiseo M et al (2010) Activity of Pemetrexed on brain metastases from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 68(2):264–268
Lee KS, Kim TS, Han J et al (1999) Diffuse micronodular lung disease: HRCT and pathologic findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr 23(1):99–106
Nagai Y, Miyazawa H, Huqun TT et al (2005) Genetic heterogeneity of the epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines revealed by a rapid and sensitive detection system, the peptide nucleic acid-locked nucleic acid PCR clamp. Cancer Res 65(16):7276–7282
Sun JM, Ahn JS, Lee S et al (2011) Predictors of skeletal-related events in non-small cell lung cancer patients with bone metastases. Lung Cancer 71(1):89–93
Uramoto H, So T, Nagata Y et al (2010) Correlation between HLA alleles and EGFR mutation in Japanese patients with adenocarcinoma of the lung. J Thorac Oncol Off Publ Int Assoc Study Lung Cancer 5(8):1136–1142
Kohno T, Tsuta K, Tsuchihara K et al (2013) RET fusion gene: translation to personalized lung cancer therapy. Cancer Sci 104(11):1396–1400.
Shigematsu H, Lin L, Takahashi T et al (2005) Clinical and biological features associated with epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations in lung cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst 97(5):339–346
Yoshida K, Yatabe Y, Park J et al (2010) Clinical outcomes of advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients screened for epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136(4):527–535
Shi Y, Au JS, Thongprasert S et al (2014) A prospective, molecular epidemiology study of EGFR mutations in asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology (PIONEER). J Thorac Oncol Off Publ Int Assoc Study Lung Cancer 9(2):154–162
Toyooka S, Matsuo K, Shigematsu H et al (2007) The impact of sex and smoking status on the mutational spectrum of epidermal growth factor receptor gene in non small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 13(19):5763–5768
Berger LA, Riesenberg H, Bokemeyer C et al (2013) CNS metastases in non-small-cell lung cancer: current role of EGFR–TKI therapy and future perspectives. Lung Cancer 80(3):242–248
Mimeault M, Batra SK (2011) Frequent gene products and molecular pathways altered in prostate cancer- and metastasis-initiating cells and their progenies and novel promising multitargeted therapies. Mol Med 17(9–10):949–964
Hiratsuka S, Watanabe A, Aburatani H et al (2006) Tumour-mediated upregulation of chemoattractants and recruitment of myeloid cells predetermines lung metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 8(12):1369–1375
Kaplan RN, Riba RD, Zacharoulis S et al (2005) VEGFR1-positive haematopoietic bone marrow progenitors initiate the pre-metastatic niche. Nature 438(7069):820–827
Umeki S (1993) Association of miliary lung metastases and bone metastases in bronchogenic carcinoma. Chest 104(3):948–950
Scagliotti GV, Hirsh V, Siena S et al (2012) Overall survival improvement in patients with lung cancer and bone metastases treated with denosumab versus zoledronic acid: subgroup analysis from a randomized phase 3 study. J Thorac Oncol Off Publ Int Assoc Study Lung Cancer 7(12):1823–1829
Rosen LS, Gordon D, Tchekmedyian S et al (2003) Zoledronic acid versus placebo in the treatment of skeletal metastases in patients with lung cancer and other solid tumors: a phase III, double-blind, randomized trial—the Zoledronic Acid Lung Cancer and Other Solid Tumors Study Group. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 21(16):3150–3157
Weilbaecher KN, Guise TA, McCauley LK (2011) Cancer to bone: a fatal attraction. Nat Rev Cancer 11(6):411–425
Yoneda T, Hiraga T (2005) Crosstalk between cancer cells and bone microenvironment in bone metastasis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 328(3):679–687
Hiraga T, Kizaka-Kondoh S, Hirota K et al (2007) Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 expression enhance osteolytic bone metastases of breast cancer. Cancer Res 67(9):4157–4163
Hung JJ, Yang MH, Hsu HS et al (2009) Prognostic significance of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, TWIST1 and Snail expression in resectable non-small cell lung cancer. Thorax 64(12):1082–1089
Normanno N, De Luca A, Aldinucci D et al (2005) Gefitinib inhibits the ability of human bone marrow stromal cells to induce osteoclast differentiation: implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of bone metastasis. Endocr Relat Cancer 12(2):471–482
Kishi Y, Kuba K, Nakamura T et al (2009) Systemic NK4 gene therapy inhibits tumor growth and metastasis of melanoma and lung carcinoma in syngeneic mouse tumor models. Cancer Sci 100(7):1351–1358
Sun YL, Liu WD, Ma GY et al (2013) Expression of HGF and Met in human tissues of colorectal cancers: biological and clinical implications for synchronous liver metastasis. Int J Med Sci 10(5):548–559
Yano S, Wang W, Li Q et al (2008) Hepatocyte growth factor induces gefitinib resistance of lung adenocarcinoma with epidermal growth factor receptor-activating mutations. Cancer Res 68(22):9479–9487
Wang W, Li Q, Takeuchi S et al (2012) Met kinase inhibitor E7050 reverses three different mechanisms of hepatocyte growth factor-induced tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in EGFR mutant lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 18(6):1663–1671
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by internal funding and the Ethics Committee of Kobe City Medical Center General Hospital. The authors would like to thank Keiko Sakuragawa for her administrative assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujimoto, D., Ueda, H., Shimizu, R. et al. Features and prognostic impact of distant metastasis in patients with stage IV lung adenocarcinoma harboring EGFR mutations: importance of bone metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis 31, 543–551 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-014-9648-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-014-9648-3