Abstract
Purpose
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is associated with adverse outcomes after acute ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). The recently proposed AKI network (AKIN) suggested modifications to the consensus classification system for AKI known as the risk, injury, failure, loss, end-stage (RIFLE) criteria. The aim of the current study was to compare the incidence and mortality (early and late) of AKI diagnosed by RIFLE and AKIN criteria in the STEMI patients undergoing primary percutaneous intervention (PCI).
Methods
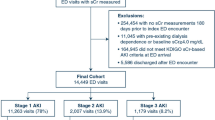
We retrospectively studied 1,033 consecutive STEMI patients undergoing primary PCI. Recruited patients were admitted between January 2008 and November 2012 to the cardiac intensive care unit with the diagnosis of acute STEMI. We compared the utilization of RIFLE and AKIN criteria for the diagnosis, classification, and prediction of mortality.
Results
The AKIN criteria allowed the identification of more patients as having AKI (9.6 vs. 3.9 %, p < 0.001) and classified more patients with stage 1 (risk in RIFLE) (7.6 vs. 1.9 %, p < 0.001) compared with the RIFLE criteria. Mortality was higher in AKI population defined by either RIFLE (46.3 vs. 6.8 %, OR 11.9, 95 % CI 6.15–23.1; p < 0.001) or AKIN (29 vs. 6.1 %; OR 6.3, 95 % CI 3.8–10.4; p < 0.001) criteria. In a multivariable logistic regression model, AKI defined with both RIFLE and AKIN was an independent predictor of both 30-day and up to 5-year all-cause mortality. However, there was no significant statistical difference in the risk provided by these two scoring systems.
Conclusions
AKIN criteria are more sensitive in defining AKI compared with the RIFLE criteria in STEMI. However, no difference exists in the mortality risk provided by these two scoring systems.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldberg A, Hammerman H, Petcherski S, Zdorovyak A, Yalonetsky S, Kapeliovich M, Agmon Y, Markiewicz W, Aronson D (2005) Inhospital and 1-year mortality of patients who develop worsening renal function following acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Am Heart J 150:330–337
Parikh CR, Coca SG, Wang Y, Masoudi FA, Krumholz HM (2008) Long-term prognosis of acute kidney injury after acute myocardial infarction. Arch Intern Med 168:987–995
Marenzi G, Assanelli E, Campodonico J, De Metrio M, Lauri G, Marana I, Moltrasio M, Rubino M, Veglia F, Montorsi P, Bartorelli AL (2010) Acute kidney injury in ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock at admission. Crit Care Med 38:438–444
Amin AP, Spertus JA, Reid KJ, Lan X, Buchanan DM, Decker C, Masoudi FA (2010) The prognostic importance of worsening renal function during an acute myocardial infarction on long-term mortality. Am Heart J 160:1065–1071
Latchamsetty R, Fang J, Kline-Rogers E, Mukherjee D, Otten RF, LaBounty TM, Emery MS, Eagle KA, Froehlich JB (2007) Prognostic value of transient and sustained increase in in-hospital creatinine on outcomes of patients admitted with acute coronary syndrome. Am J Cardiol 99:939–942
Bellomo R, Ronco C, Kellum JA, Mehta RL, Palevsky P (2004) Acute renal failure—definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: the Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit Care 8:R204–R212
Uchino S, Bellomo R, Goldsmith D, Bates S, Ronco C (2006) An assessment of the RIFLE criteria for acute renal failure in hospitalized patients. Crit Care Med 34:1913–1917
Ahlstrom A, Kuitunen A, Peltonen S, Hynninen M, Tallgren M, Aaltonen J, Pettila V (2006) Comparison of 2 acute renal failure severity scores to general scoring systems in the critically ill. Am J Kidney Dis 48:262–268
O’Riordan A, Wong V, McQuillan R, McCormick PA, Hegarty JE, Watson AJ (2007) Acute renal disease, as defined by the RIFLE criteria, post-liver transplantation. Am J Transplant 7:168–176
Guitard J, Cointault O, Kamar N, Muscari F, Lavayssiere L, Suc B, Ribes D, Esposito L, Barange K, Durand D, Rostaing L (2006) Acute renal failure following liver transplantation with induction therapy. Clin Nephrol 65:103–112
Ostermann M, Chang RW (2007) Acute kidney injury in the intensive care unit according to RIFLE. Crit Care Med 35:1837–1843 (quiz 1852)
Bagshaw SM, George C, Dinu I, Bellomo R (2008) A multi-centre evaluation of the RIFLE criteria for early acute kidney injury in critically ill patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:1203–1210
Mehta RL, Kellum JA, Shah SV, Molitoris BA, Ronco C, Warnock DG, Levin A (2007) Acute kidney injury network: report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit Care 11:R31
Bruetto RG, Rodrigues FB, Torres US, Otaviano AP, Zanetta DM, Burdmann EA (2012) Renal function at hospital admission and mortality due to acute kidney injury after myocardial infarction. PLoS One 7:e35496
Hsieh MJ, Chen YC, Chen CC, Wang CL, Wu LS, Wang CC (2013) Renal dysfunction on admission, worsening renal function, and severity of acute kidney injury predict 2-year mortality in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circ J 77:217–223
Hwang SH, Jeong MH, Ahmed K, Kim MC, Cho KH, Lee MG, Ko JS, Park KH, Sim DS, Yoon NS, Yoon HJ, Kim KH, Hong YJ, Park HW, Kim JH, Ahn YK, Cho JG, Park JC, Kang JC (2011) Different clinical outcomes of acute kidney injury according to acute kidney injury network criteria in patients between ST elevation and non-ST elevation myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol 150:99–101
Marenzi G, Cabiati A, Bertoli SV, Assanelli E, Marana I, De Metrio M, Rubino M, Moltrasio M, Grazi M, Campodonico J, Milazzo V, Veglia F, Lauri G, Bartorelli AL (2013) Incidence and relevance of acute kidney injury in patients hospitalized with acute coronary syndromes. Am J Cardiol 111:816–822
O’Gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD, Casey DE Jr, Chung MK, de Lemos JA, Ettinger SM, Fang JC, Fesmire FM, Franklin BA, Granger CB, Krumholz HM, Linderbaum JA, Morrow DA, Newby LK, Ornato JP, Ou N, Radford MJ, Tamis-Holland JE, Tommaso CL, Tracy CM, Woo YJ, Zhao DX, Anderson JL, Jacobs AK, Halperin JL, Albert NM, Brindis RG, Creager MA, DeMets D, Guyton RA, Hochman JS, Kovacs RJ, Ohman EM, Stevenson WG, Yancy CW (2012) 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association task force on practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol 61:e78–e140
Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D (1999) A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation: modification of diet in Renal Disease Study Group. Ann Intern Med 130:461–470
Board NKFNKDOQIKDA (2002) K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis 39:S1–S266
Koreny M, Karth GD, Geppert A, Neunteufl T, Priglinger U, Heinz G, Siostrzonek P (2002) Prognosis of patients who develop acute renal failure during the first 24 hours of cardiogenic shock after myocardial infarction. Am J Med 112:115–119
Marenzi G, Assanelli E, Campodonico J, Lauri G, Marana I, De Metrio M, Moltrasio M, Grazi M, Rubino M, Veglia F, Fabbiocchi F, Bartorelli AL (2009) Contrast volume during primary percutaneous coronary intervention and subsequent contrast-induced nephropathy and mortality. Ann Intern Med 150:170–177
Marenzi G, De Metrio M, Rubino M, Lauri G, Cavallero A, Assanelli E, Grazi M, Moltrasio M, Marana I, Campodonico J, Discacciati A, Veglia F, Bartorelli AL (2010) Acute hyperglycemia and contrast-induced nephropathy in primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Am Heart J 160:1170–1177
Weisbord SD, Chen H, Stone RA, Kip KE, Fine MJ, Saul MI, Palevsky PM (2006) Associations of increases in serum creatinine with mortality and length of hospital stay after coronary angiography. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:2871–2877
Fox CS, Muntner P, Chen AY, Alexander KP, Roe MT, Wiviott SD (2012) Short-term outcomes of acute myocardial infarction in patients with acute kidney injury: a report from the national cardiovascular data registry. Circulation 125:497–504
Bagshaw SM, George C, Bellomo R (2008) A comparison of the RIFLE and AKIN criteria for acute kidney injury in critically ill patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:1569–1574
Lopes JA, Fernandes P, Jorge S, Goncalves S, Alvarez A, Costa e Silva Z, Franca C, Prata MM (2008) Acute kidney injury in intensive care unit patients: a comparison between the RIFLE and the acute kidney injury network classifications. Crit Care 12:R110
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Working Group (2013) KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guidelines for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl 7(1):1–150
Coca SG, Yalavarthy R, Concato J, Parikh CR (2008) Biomarkers for the diagnosis and risk stratification of acute kidney injury: a systematic review. Kidney Int 73(9):1008–1016
Koyner JL, Parikh CR (2013) Clinical utility of biomarkers of AKI in cardiac surgery and critical illness. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 8(6):1034–1042
Conflict of interest
None on the part of any author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shacham, Y., Leshem-Rubinow, E., Ziv-Baran, T. et al. Incidence and mortality of acute kidney injury in acute myocardial infarction patients: a comparison between AKIN and RIFLE criteria. Int Urol Nephrol 46, 2371–2377 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-014-0827-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-014-0827-6